It is now simpler than ever to report a power cut. If you want to report a power cut call...
Generation Heat Map
Use the icons to display areas of high, medium and low availability/demand.
Use the icons to display the specific supply types.
Roll over a supply type to see the post code it covers.
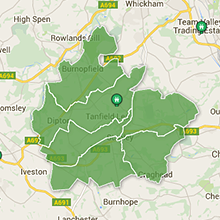
Click on a supply type to find out related information.
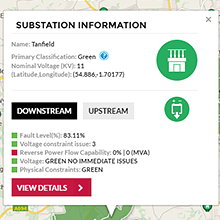
Choose to view downstream (availability)
or upstream (demand) information.















